Table of Contents
Fertilization & Fertilizers – Why
The soil requires the recovery of nutrients through fertilization to obtain healthy plants and a good harvest. Let’s see the different types of fertilizers, when and how to fertilize.
Soil quality is a key factor for a healthy plant and a good crop. From the soil, plants remove the macro and micro components of nutrients necessary to develop. Whether the soil has been used extensively or not, nutrient deficiency requires minerals that will be returned to the soil through fertilization. Let’s see different types of fertilizer, when and how to fertilize.
To know how to fertilize plants correctly, you just need to know what types of fertilizers exist and what is the purpose of each one of these fertilizers. Do you want to bring back soil fertility and offer full development for your harvest? Check out our tips!
Different Types of Fertilizers
Classified on the origin of the nutrients:
Vegetable (could be vegan or not)
Animal
Mineral origin
Classified on the chemical ingredients:
1 – Organic fertilizers
2 – Chemical (or inorganic) fertilizers
The choice of fertilizer depends on the nutrient necessities of the plant and the soil and may be of vegetable, animal, or mineral origin.
The decision when choosing an organic and inorganic fertilizer can be based on how quickly the effect needs to take place. In the case of food crops, the decision may be influenced by the need to also look for organic crops and suitable for vegans or vegetarians.
Different Types of Fertilizers: Organic Fertilizers
It could be obtained from vegetable or animal material. Organic fertilizers are slower acting than inorganic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers need to decompose before acting on the plants. Usually used for home and organic gardens. They can be elaborated through composting.
Organic fertilizers can be enriched with inorganic nutrients, resulting in a mixture of organic and inorganic fertilizer and they are great alternatives increasing productivity and contributing to soil biodiversity.
Examples of organic fertilizers: dung, bone meal, vegetable remains earthworm humus or organic liquid fertilizer obtained by composting with worms, fiber such as bran, and plant debris removed from the soil.
- Package contains 16 Pounds organic all purpose plant fertilizer grains and is produced to avoid wasteful runoff, mess, hazards and smells
- Plant fertilizer is formulated with a 4-4-4 NPK to provide vegetables, plants, and flowers nutrients they need for a high yield and vibrant foliage
- Jobe's organic fertilizer contains no synthetic chemicals and are OMRI listed for organic gardening by the USDA
Different Types of Fertilizers: Chemical (or Inorganic) Fertilizers
Contrasting organic fertilizers, chemical fertilizers are obtained from minerals, natural sources, or oil. The main nutrients needed for plant development are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, usually called NPK fertilizers for the letter assigned to each element.
Chemical or inorganic fertilizers are rapid absorption and fast-acting, no need to wait until the decomposing process. All elements are ready to be incorporated for the plant through the soil. Chemical or inorganic fertilizers accelerated the development of cultivation and harvest. It is possible to calculate exactly the amount of nutrients needed according to the deficiencies of the plant and soil.
The disadvantage of using chemical or inorganic fertilizers is the damage if it is in excess or overuse. It can cause soil problems by altering the chemical composition of the soil, making it unproductive and causing irreversible damage. Excess of inorganic fertilizers can cause atypical plant development, as well as burns, wilting, and root rot.
- 20-10-20 Analysis - Great for producing vibrant green leaves, strong branches, and more fruit in tropical fruiting plants.
- Many Ways to Feed - Citrus FeED can be used as a foliar or root feeding product. Great for spraying directly onto leaves, roots, or when used in a continuous feed system.
- Water-Soluble Powder – Powdered concentrates go further than liquid fertilizers. Simply mix your measured powder with water and you are ready to feed with multiple gallons of liquid fertilizer!
When and How to Fertilize Different Cultivation
Lighting, watering, and irrigation are key processes for cultivation. However, some crops will need help with fertilizers to develop fully. Some plant processes will need help and different proportions of fertilizers.
Are your plants lacking nutrients? Observe the leaves to see if the soil is nutritionally deficient. The image below will help you to identify the deficiencies of certain nutrients. Learn more Here.
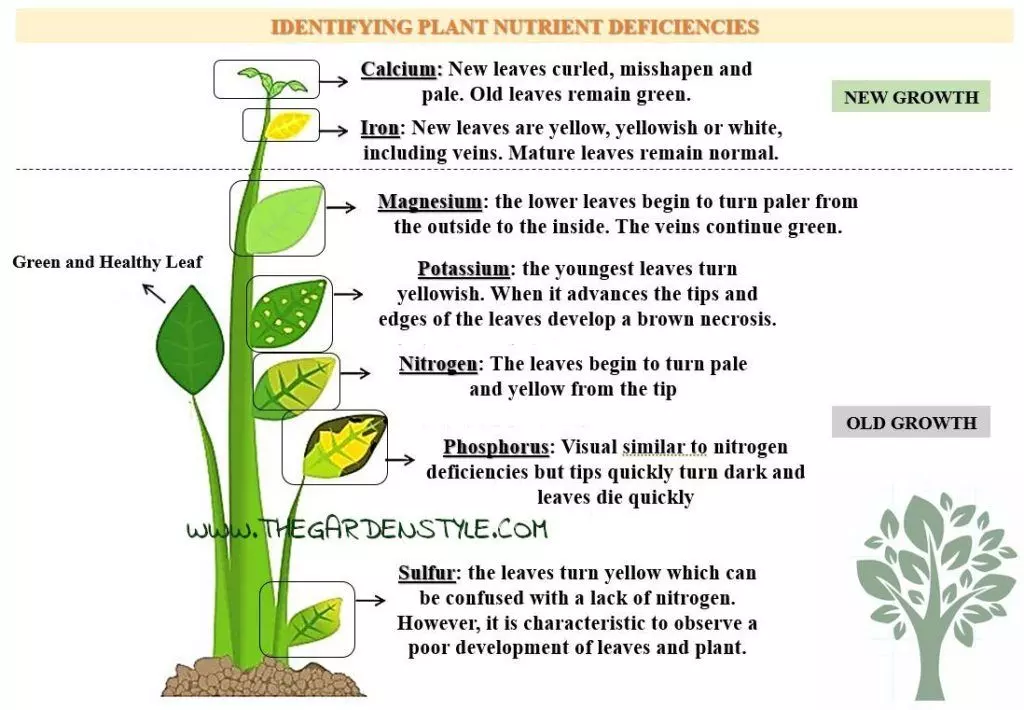
Solve Nutritional Deficits in the Soil
To solve nutritional deficits in the soil and ensure nutrients necessary to develop and to obtain a good harvest, a wide variety of options are presented as fertilizers. It should be a balanced combination between the types of fertilizer and the assurance of the correct growth of your domestic crops. Here’s how to solve it!
How to Fertilize Plants
Food crops: Vegetables and Fruit Trees
When is the best time to fertilize food crops? Late winter or early spring.
How often: every 6 months.
Fertilizer: Organic fertilizers are the best option, such as blood meal, bone meal, soybean meal, composted manure, worm composting, cottonseed meal, and any other organic-rich in nitrogen. Phosphorus will be needed to stimulate the appearance of fruits and flowers.
Another option could be applying chemical or inorganic fertilizers such as NPK with the amount indicated on the packaging. Remember that overuse could affect and kill the culture.

Floriferous
When is the best time to fertilize Floriferous? During blooming time
How often: every 2 to 3 months.
Fertilizer: Controlled release chemical fertilizer for a quick result. Organic fertilizers such as earthworm humus, organic liquid of composting, blood meal, bone meal, and bovine manure, are also great alternatives, with no risk of overdose.

Foliage
When is the best time to fertilize Foliage? At any time
How often: every 3 to 4 months.
Fertilizer: Chemical or inorganic fertilizer, options that can be diluted in the water used during watering ais a good option. Organic fertilizers are always an option as well.




